
Ways To Mimic Calorie Restriction
Calorie Restriction Mimetics (CRMs) are compounds that can induce the same mechanisms as eating less, without having to actually eat less. R
In this, post we will discuss how to have your cake (food) and eat it too..
Contents:
- Basics
- Benefits Of CRMs/Fasting Mimetics
- Real Life Examples Of Fasting
- List Of Caloric Restriction Mimetics
- What Goes Well With Calorie Restriction Mimetics?
- Mechanism Of Action
Basics
What Defines A CRM?
CRMs should: R
- Mimic the metabolic, hormonal and physiological effects of CR
- Don’t significantly decrease long-term food intake
- Activate stress–response pathways, as observed in CR, and protect against a variety of stressors
- Reduce inflammation and autoimmunity.
Benefits Of CRMs/Fasting Mimetics
Mimicking CR/Fasting may improve:
- Adaptability to Stress (CR acts on hormesis via NRF2) R R R
- Autophagy (improve stem cells) R R R R
- Body Fat Mass R R
- Cardiovasuclar Function R R R
- Eyesight/Ocular Health R R
- Healthspan R R
- Immune Function R
- Insulin Sensitivity R R
- Kidney Function R
- Leptin Sensitivity R
- Lifespan R
- Liver Function R
- Memory (is Alzheimer’s) R
- Metabolism (may help with hypoxia) R R
- Mitochondrial Function R
- Muscle R
- NAD levels R R
- Neurogenesis R
- Prevention of Cancer and Anti-tumor Efficacy (of chemotherapy) R R R R
- Skin and Wound Healing R
Some CRM’s can mimic exercise or even synergize well with exercise and improve muscle function. R R
Real Life Examples Of Caloric Restriction
Compared to the rest of the Japanese population, inhabitants of Okinawa who followed a low-calorie diet over a prolonged period of time show to have a longer lifespan and an increased healthspan. R
They eat a mildly caloric restricted diet (10-15%) and high consumption of foods that may mimic the biological effects of caloric restriction, including sweet potatoes, marine-based carotenoid-rich foods, and turmeric. R
List Of Calorie Restriction Mimetics

These CRMs work on the mechanisms of calorie restriction.
Dietary/Mechanical Strategies (that aren’t calorie restriction):
- Amino Acid Restriction R
- Avocado (Mannoheptulose) R
- Bariatric Surgery R
- Cinnamon (Methylhydroxychalones) R
- Coffee R
- Intermittent Fasting/Feeding R
- Olive Oil (Tyrosol) R
- Rosemary (Rosmarinic Acid) R
- Sesame (Sesamin) R
- Tomatoes (Tomatidine) R
- Turmeric (Curcumin) R
Supplements:
- Allantoin R
- Allulose R
- Ashwaganda (Withaferin A) R
- Astaxanthin R
- BCAAs (Leucine can increase mitochondrial mass in human muscle cells) R R
- Caffeic acid R
- Caffeine R
- Carnitine R
- Chitosan (Inhibiting Nutrient Absorption) R
- EGCG R R
- Fisetin R R
- Ginseng (Ginsenosides) R
- Glucosamine R
- Gymnema R
- Gynostemma (jiaogulan)
- Hesperidin R
- Kaempferol R
- Ketones R
- Kokum (Garcinia Indica) R
- Lactoferrin R
- Licorice (isoliquiritigenin) R
- Lipoic Acid (weak) R
- Mannan Oligosaccharides (Inhibiting Nutrient Absorption) R
- MitoQ R
- NAC R
- Naringenin R
- Nicotinamide Riboside R
- Olestra R
- Polydatin R
- Quercetin R
- Resveratrol R
- Thundergod Vine (Celastrol) R
- Ursolic acid (ie holy basil, thyme, rosemary) R
Hormones:
- Adiponectin (binding to AdipoR1 and AdipoR2)
- Irisin R
- Leptin (possibly lower) R
- Melatonin R
- Meteorin-like R
- NPY R
- Resistin (lower levels) R
Drugs:
- Acarbose (Inhibiting Nutrient Absorption) R
- Allantoin R
- AICAR R
- Aspirin R
- Bezafibrate R
- Dapsone R
- Epitalon R
- Exanadin
- GW1516 R
- Hydroxycitrate (citric acid) R
- LY‐294002 R
- Metformin R R
- Olbetam (niacin derivative)
- Orlistat (Inhibiting Nutrient Absorption) R
- Oxaloacetic acid R
- Pioglitazone R
- Rapamycin R
- Rimonabant
- Rosiglitazone (modulation PPARs leptin/adiponectin)
- SARMs (some) R
- Sodium phenylbutyrate
- Spermidine R
- SRT1720 R
- Trichostatin A (TSA) R
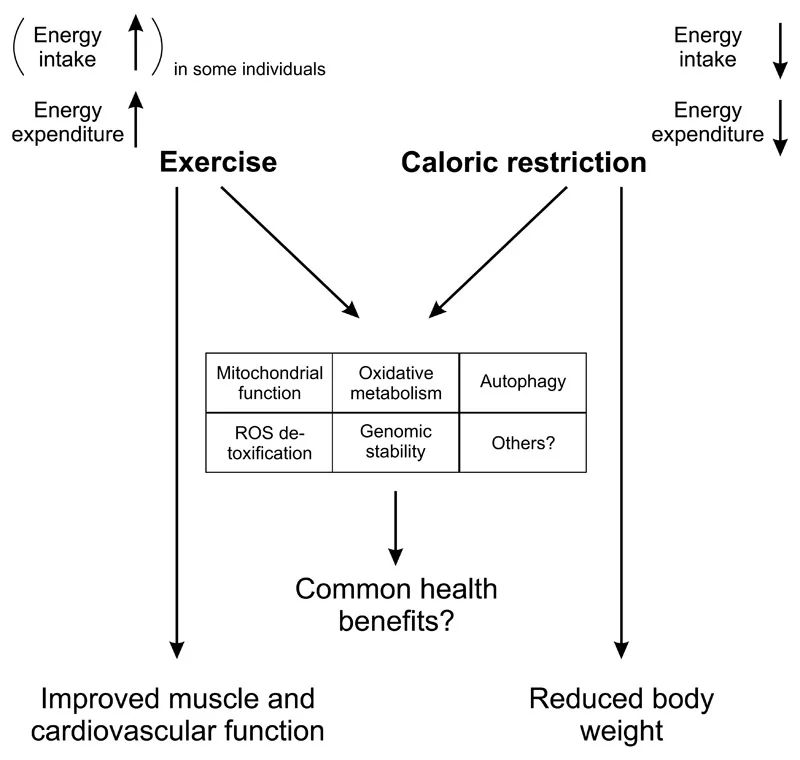
What Goes Well With Calorie Restriction Mimetics?
Exercise Mimetics may go well with CRMs.
Mechanism Of Action
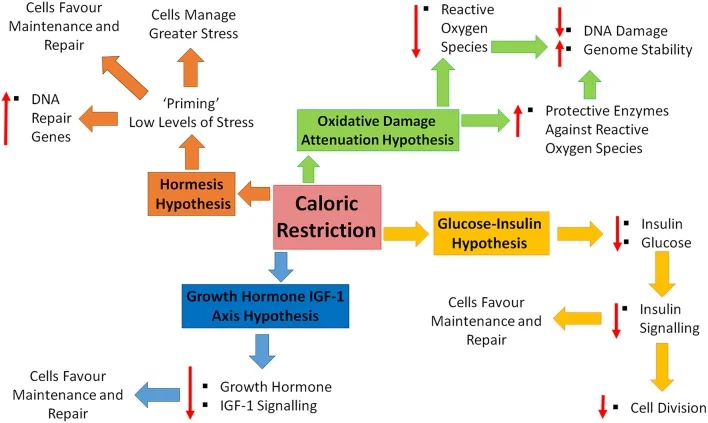
Some Mechanisms / Pathways Of CR Mimetics
Working on these mechanisms may also help mimic CR:
- Increasing AMPK R R
- Increasing cAMP R
- Increasing ERRγ R
- Increasing FGF21 R R
- Increasing FOXO R
- Increasing HSF1 R
- Increasing LKB1 R
- Increasing NO -> HSP R
- Increasing NRF1 R
- Increasing NRF2 R
- Increasing NR3C4 R
- Increasing PNC-1 R
- Increasing PPARβ/δ R R
- Increasing PGC-1α R
- Increasing REV-ERBα R
- Increasing SIRTs (and other STACs, ie fisetin) R R
- Increasing SOD R
- Increasing UCP2 and UCP3 R
- Inhibiting ActRIIB R
- Inhibiting DPP-4
- Inhibiting Glycolysis R
- Inhibiting HDACs 1 and 2 R
- Inhibiting mTOR R R
- Inhibiting Myostatin R
- Reduces AGEs R
- Reduces FAO R
- Reduces GH R
- Reduces HMG-Co-A reductase R
- Reduces IGF1 R
Advanced:
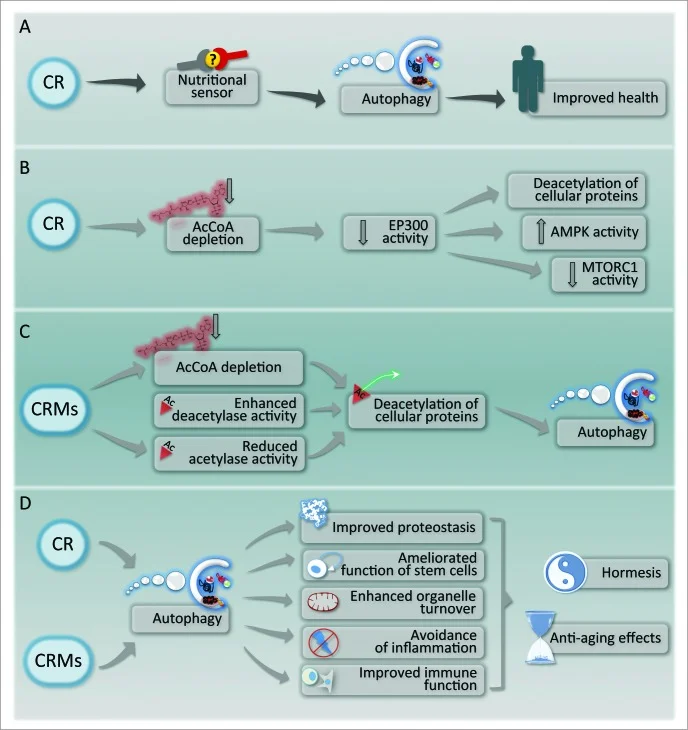
- Nutrient depletion, which is one of the physiological triggers of autophagy, results in the depletion of intracellular acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) coupled to the deacetylation of cellular proteins (3 ways). RR
- The depletion of cytosolic AcCoA by interfering with its biosynthesis
- The inhibition of acetyltransferases, which are enzymes that transfer acetyl groups from AcCoA to other molecules, mostly leucine residues in cellular proteins
- The stimulation of deacetylases, which catalyze the removal of acetyl groups from leucine residues.
- CRMs deplete regulatory T Cells from tumor bed and trigger an autophagy-dependent anticancer immune response. R
- In the liver, AdipoR1 activates the AMPK pathways and AdipoR2 activates PPARα pathways. R
- AMPK enhances SIRT1 activity by increasing cellular NAD+ levels, resulting in the deacetylation and modulation of the activity of downstream SIRT1 targets such as PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and forkhead box O1 (FoxO1), and is regulated by adiponectin–adipoR1 system. R
- CR induces the function of the pyrazinamidase/nicotinamidase 1 (PNC-1) enzyme which deaminates and depletes nicotinamide. R




